Eman Sakina
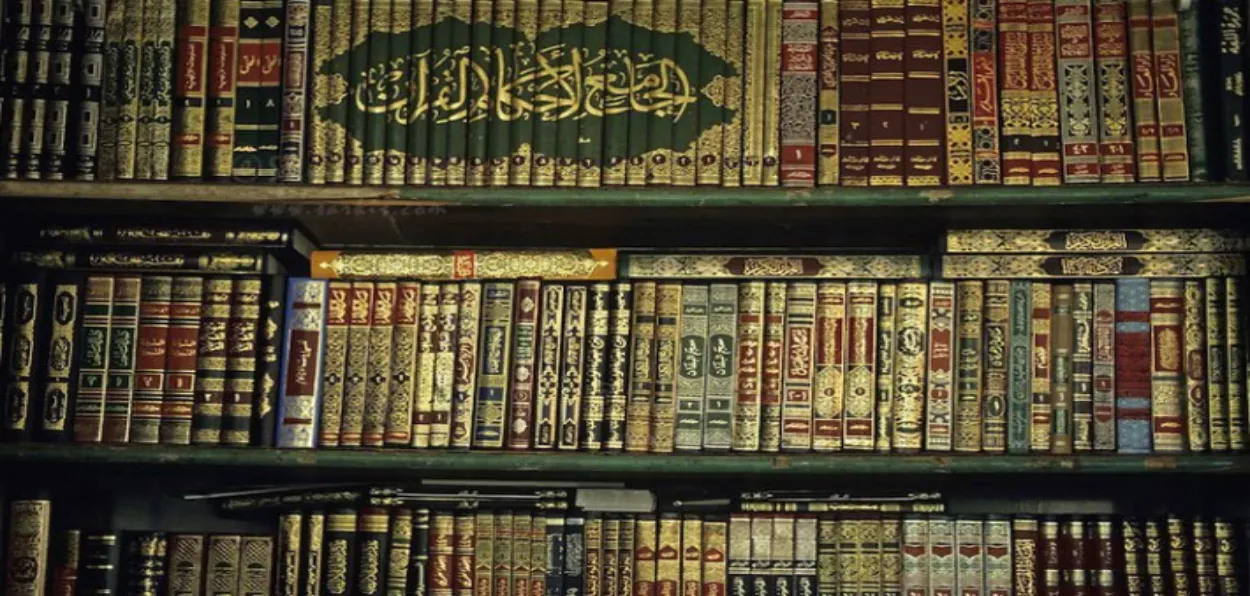
Islamic libraries have played a pivotal role in the preservation and transmission of knowledge throughout history, significantly influencing various fields, such as science, philosophy, medicine, and literature. Their contributions continue to reverberate in contemporary society, enriching intellectual pursuits and fostering cultural exchanges.
Friday Musings
As we face the challenges of the modern world, the role of these libraries remains vital, reminding us of the richness of our shared intellectual heritage and the importance of fostering an environment of learning and dialogue. The legacy of Islamic libraries continues to shape contemporary scholarship, encouraging the pursuit of knowledge and understanding across cultures.
The emergence of Islamic libraries can be traced back to the early centuries of Islam (7th-9th centuries). As the Islamic empire expanded, cities like Baghdad, Cordoba, Cairo, and Damascus became centres of learning. The House of Wisdom (Bayt al-Hikma) in Baghdad, founded during the Abbasid Caliphate, exemplified the commitment of Muslim scholars to collect, translate, and study texts from various civilisations, including Greek, Persian, and Indian sources. The establishment of such libraries was not merely infrastructural; they symbolised the Islamic commitment to knowledge and scholarship.
Functions of Islamic Libraries
Preservation of Manuscripts: Islamic libraries collected and preserved invaluable manuscripts, which would have otherwise been lost. These texts included religious scriptures, philosophical treatises, scientific works, poetry, and histories. The meticulous work of scribes ensured that knowledge was passed down through generations, creating a reservoir of wisdom.
Translation Movements: One of the most significant contributions of Islamic libraries was facilitating translation movements. Scholars translated texts from Greek, Latin, Sanskrit, and other languages into Arabic. This not only enriched the Arabic language but also introduced new ideas and concepts that were critical to the development of various disciplines.
Educational Centres
Islamic libraries often served as educational hubs, where scholars and students gathered to study and engage in intellectual discussions. Institutions like Al-Qarawiyyin in Morocco and Al-Azhar in Egypt became renowned centres of higher learning, where students could access a vast array of resources and learn from esteemed scholars.
eNetworkof Knowledge Exchange: The Islamic Golden Age saw a significant exchange of knowledge across cultures. Libraries acted as conduits for scholarly communication, fostering collaboration among Muslim, Jewish, and Christian scholars. This intercultural dialogue contributed to advancements in mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy.
Promotion of Scientific Inquiry
Islamic libraries were instrumental in promoting scientific inquiry and critical thinking. By facilitating access to various texts, they encouraged scholars to question established norms, conduct experiments, and seek empirical evidence. Notable figures, such as Al-Farabi, Ibn Sina (Avicenna), and Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen), made substantial contributions to their fields, influenced by the resources available in these libraries.
In contemporary times, the legacy of Islamic libraries endures as they adapt to the digital age. Many libraries are digitising their collections, making knowledge accessible globally. Initiatives like the "Islamic Heritage Project" aim to preserve rare manuscripts and foster a deeper understanding of Islamic civilisation.
ALSO READ: Why India must not worry too much about the Saudi-Pak defence pact
Moreover, Islamic libraries continue to play a vital role in fostering intellectual curiosity and promoting intercultural dialogue. They serve as spaces for community engagement, offering programs that encourage the exploration of Islamic history, culture, and thought.